Low-Level Fusion and Perception for NCAP and GSR – Part 2

Download Complete White Paper in PDF Format
Part 1 of this white paper series analyzed the evolution of road safety and the growing importance of ADAS. It considered the different maturity levels of new car assessment programs worldwide, highlighting the various agencies that have been quick to evolve their assessment programs to incorporate additional ADAS testing. In Part 2, we look to understand the testing requirements for new vehicles regarding automated driver assistance systems (ADAS) under new car assessment programs (NCAP). This post delivers an overview of the scenarios, conditions, and environments in which testing is performed and takes a forward-looking approach to delve into how ADAS testing for NCAP will evolve over the coming years and the stresses such an evolution puts on sensor fusion and perception systems. Finally, it examines LeddarTech’s low-level sensor fusion and perception technology and how it handles NCAP testing to enable OEMs and Tier 1-2 suppliers to deliver 5-star safety-rated vehicles to consumers.
Testing Requirements of NCAP Today
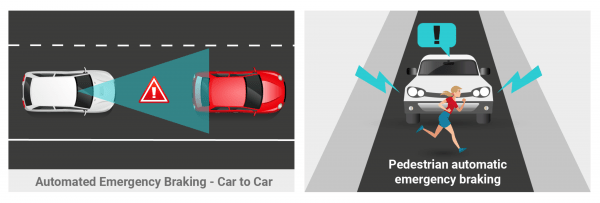
For a vehicle to rank well on NCAP ADAS tests, its fusion and perception system must perform well under a myriad of conditions and show strong performance on multiple criteria under multiple scenarios. For example, Euro NCAP introduced automated emergency braking (AEB) ADAS testing involving car-to-car crashes. Some of the scenarios in which the vehicle must be tested are car-to-car rear stationary (CCRs), car-to-car rear moving (CCRm) and car-to-car rear braking (CCRb). Testing is further complicated by the multitude of tests performed on the vehicle by changing one or more test conditions, such as test vehicle speed, object speed and angle of introduction.
The test protocol also specifies the weather conditions, brake warm-up procedure, tire conditions and many other requirements before testing. Euro NCAP AEB C2C Test Protocol v4.1.1 stipulates that ADAS tests be conducted in dry conditions with wind speeds below 10 m/s and homogeneous natural ambient illumination across the test area. Furthermore, it prescribes that tests not be performed driving towards or away from the sun when there is direct sunlight.
Future Testing Requirements of NCAP and the Challenges Therein
The future of ADAS testing under NCAP is marked by lower error margins, increased complexity and varied testing. Existing test protocols, while robust, test vehicles under best-weather conditions. Future testing of NCAP will incorporate night-time and inclement weather testing such as low light and/or heavy precipitation, fog or snow, and varying degrees of traction/reflectivity of the surface to simulate actual driving conditions faced by drivers.
Given the challenges that lie ahead, sensor fusion and perception solutions must perform well across varied environments, conditions and scenarios. Such systems must be scalable and sensor-agnostic so that future advancements in ADAS can be built on the same platform, reducing rework needs and incorporate everchanging sensor architecture. A scalable system reduces R&D time and cost for OEMs and Tier 1-2s, enabling them to go to market faster and deliver these life-saving technology to the masses. Most importantly, perception systems must remain cost-effective while delivering high performance.
Low-Level Sensor Fusion to Enable 5-Star Safety Rating
High performance and cost-effectiveness are two key elements in democratizing safety. Today, LeddarTech enables OEMs and Tier 1-2s to unlock new levels of perception performance by leveraging proprietary low-level fusion and perception technology. LeddarTech has delivered two comprehensive front-view products, LVF-E (entry) and LVF-H (high), that cost-effectively provide the performance required to reach 5-star safety ratings.
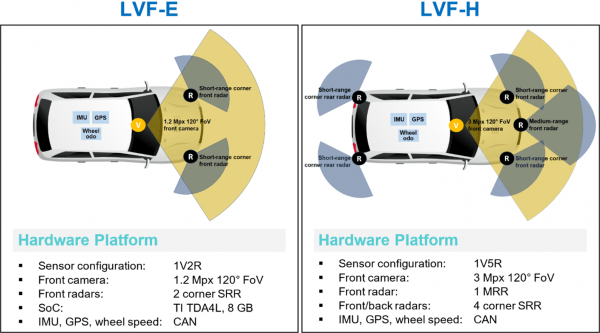
LeddarVision perception stack extends safety features support with detected objects trajectory prediction, perception decomposition and ODD analysis, and extends the supported object detection range to over 200 m. LVF-H’s superior object detection performance extends to occluded VRUs and vehicles, providing early warning in NCAP-tested scenarios (e.g., occluded cyclist tests). Its ability to detect and track objects under poor weather conditions such as fog, rain and snow and even when the camera is saturated against direct sunlight makes safe and reliable ADAS a reality. In addition, the system’s capability to detect and track objects if the camera fails and to continue operation despite a dirty lens are examples of how LeddarVision outperforms legacy object-level fusion solutions and realizes strong NCAP performance. LeddarVision’s demonstrated performance in reducing false alarms, small object detection, superior object separation and position measurement accuracy in highway scenarios form the basis of a perception system designed to deliver a 5-star safety rating.
Summary
Road safety has undergone and continues to experience incremental changes. Vehicle safety solutions have traditionally revolved around mechanical innovations such as airbags, seatbelts and stronger frames. However, the future of road safety will be determined by a vehicle’s ability to avoid or mitigate an accident, and to achieve this a robust performing fusion and perception software is required. The perception system must be scalable, offer high performance in a variety of scenarios, conditions and and environments, and be cost-effective to accelerate adoption. LeddarTech’s two front-view products (LVF-E and LVF-H) are two distinct comprehensive low-level fusion and perception software products that optimally combine sensor modalities for Level 2/2+ ADAS applications to enable a 5-star NCAP 2025/GSR 2022 rating.
Click HERE to see Part one of this two-part white paper series
Download Complete White Paper in PDF Format
This White Paper does not constitute a reference design. The recommendations contained herein are provided “as is” and do not constitute a guarantee of completeness or correctness. LeddarTech® has made every effort to ensure that the information contained in this document is accurate. Any information herein is provided “as is.” LeddarTech shall not be liable for any errors or omissions herein or for any damages arising out of or related to the information provided in this document. LeddarTech reserves the right to modify design, characteristics and products at any time, without notice, at its sole discretion. LeddarTech does not control the installation and use of its products and shall have no liability if a product is used for an application for which it is not suited. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate products for your application, (2) validating, designing and testing your application and (3) ensuring that your application meets applicable safety and security standards. Furthermore, LeddarTech products are provided only subject to LeddarTech’s Sales Terms and Conditions or other applicable terms agreed to in writing. By purchasing a LeddarTech product, you also accept to carefully read and to be bound by the information contained in the User Guide accompanying the product purchased.