
Download Complete White Paper in PDF Format
The USA’s National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) recently proposed amendments to its new car assessment program (NCAP), overhauling its testing of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) for safer roads. The proposed changes include adding four new ADAS features and modifying the existing test criteria for the lane departure warning (LDW) feature. The four ADAS technologies proposed are blind spot detection (BSD), blind spot intervention (BSI), lane keeping support (LKS) and pedestrian automatic emergency braking (PAEB). In addition, for the first time in its history, U.S. NCAP will extend to enhance the protection of pedestrians through the addition of PAEB. LeddarTech, an automotive software provider that enables ADAS and AD, applauds the PAEB’s initiative as an essential element of road safety and encourages an expanded testing program of ADAS applications under extended conditions, including and not limited to weather changes.
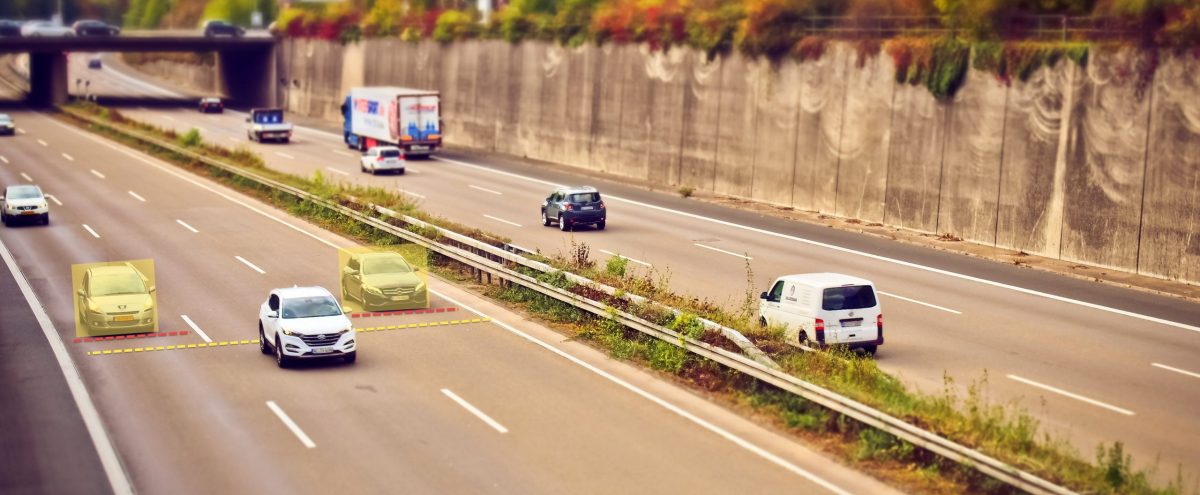
Blind spot detection and intervention systems use a radar-camera architecture to detect vehicles in a car’s blind spots. NHTSA has proposed three test procedures for blind spot warning systems: the straight-line converge test, the straight-line diverge test and the straight-lane drive-by test. Each test is performed from the left and right of the vehicle and the blind spot warning must be presented to the driver within 300 milliseconds of the vehicle entering the blind spot zone.
Adding PAEB to the NCAP is a significant step forward in pedestrian safety. The system detects potential collisions with pedestrians or bicyclists while the car is traveling and automatically applies brakes to avoid or mitigate a collision. PAEB covers four common pedestrian crash scenarios when a vehicle is:
Scenarios 1 and 4 are proposed for inclusion in U.S. NCAP, but not scenarios 2 and 3 due to concerns by commenters over a significant number of false positive detections and that sensors would need an expanded field of view.
Lane departure warning systems typically use a camera-only solution to detect when a car has veered out of its lane. The existing NCAP test procedure for LDW systems does not include testing the system in adverse visibility conditions, such as rain, snow, hail, fog, smoke or ash. The camera must not be saturated during tests, such as when the sun is oriented 15 degrees or less from the horizontal. In December 2015, the NHTSA highlighted concerns about missed detections resulting from reflecting sunlight, lines being covered with water or other unforeseen anomalies resulting in missed detections. The agency was also concerned about consumers disabling LDW due to high false positive rates and sought feedback from the industry. NHTSA proposes changes in testing requirements and performance benchmarks to increase adoption and discourage disabling.
LeddarTech’s front-view and surround-view perception products based on low-level sensor fusion have shown reduced false alarms in performance testing and enable turn-assist applications for a safer road. Additionally, LeddarTech has demonstrated strong performance in adverse conditions such as rain, snow, fog and direct sunlight that render a camera useless or degraded.
LeddarTech supports the proposed updates to the U.S. NHTSA’s NCAP as a significant step forward in enhancing road safety for all road users. As engineers working on advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous driving, it is crucial to keep updated with these proposed changes to ensure that we create safe and reliable systems for all road users.
LeddarTech’s low-level fusion and perception software solution, LeddarVision™, is a high-performance, cost-effective, hardware-agnostic and scalable solution that delivers accurate 3D environmental models. This scalable software supports all SAE autonomy levels by applying AI and computer vision algorithms to fuse raw data from sensors employed in L2 to L5 applications. Its low-level or raw data fusion technology detects very small obstacles on the road with better detection rates and fewer false alarms than legacy “object fusion” solutions. Unclassified obstacles are also detected, providing an additional layer of safety to the vehicle. LeddarVision helps to resolve many limitations of existing ADAS perception architectures and provides superior performance, often surpassing object-level fusion performance in adverse scenarios.
LeddarTech recently released the LeddarVision Front-View (LVF) product family for customers seeking to develop entry-level ADAS safety and highway assistance. The LVF-E, LVF-H and LVS-2+ are three distinct front-view and surround-view comprehensive low-level fusion and perception software stacks that optimally combine sensor modalities to enable Level 2/2+ ADAS applications achieving a 5-star NCAP 2025/GSR 2022 rating.
Download Complete White Paper in PDF Format
This White Paper does not constitute a reference design. The recommendations contained herein are provided “as is” and do not constitute a guarantee of completeness or correctness. LeddarTech® has made every effort to ensure that the information contained in this document is accurate. Any information herein is provided “as is.” LeddarTech shall not be liable for any errors or omissions herein or for any damages arising out of or related to the information provided in this document. LeddarTech reserves the right to modify design, characteristics and products at any time, without notice, at its sole discretion. LeddarTech does not control the installation and use of its products and shall have no liability if a product is used for an application for which it is not suited. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate products for your application, (2) validating, designing and testing your application and (3) ensuring that your application meets applicable safety and security standards. Furthermore, LeddarTech products are provided only subject to LeddarTech’s Sales Terms and Conditions or other applicable terms agreed to in writing. By purchasing a LeddarTech product, you also accept to carefully read and to be bound by the information contained in the User Guide accompanying the product purchased.
E-Book – This complimentary e-book explains the main features and components of the LeddarVision sensor fusion and perception solution for automotive and mobility ADAS and autonomous driving.

White Paper – This post introduces to new car assessment programs (NCAP), the role played in enabling road safety and the various NCAP programs across the world, with a specific focus on how the U.S. and Europe have embraced technology in their new car assessment programs and the growing importance of automated driver assistance systems (ADAS).
PODCAST – “There is a difficult compromise between intervention for an actual hazard, what we call true positives, and false interventions, or false positives,” Palao said. “This is a fine balance that you need to keep in mind to design the systems so that your system will account for the vast majority of situations in which you are exposed to danger. On the flip side, you don’t want your car to break for every situation you encounter on the roads.”
Application Note – This note provides the reader with an understanding of the testing requirements for new vehicles regarding advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) under new car assessment programs (NCAP). It delivers an overview of the scenarios, conditions and environments in which testing is performed, and takes a forward-looking approach to delve into how ADAS testing for NCAP will evolve over the coming years.